The openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager (CKM) is a unique resource for the specification of health information that will become part of people's lifelong health record. The work raises questions. What more do we need to develop and manage high quality specifications for health information suitable for sharing between clinical applications? How do we manage the tension between harnessing the richness of contributions from the large and enthusiastic community of clinicians and health informaticians and ensuring that the specifications are comprehensive and internally consistent? This has been weighing on my mind over the past couple of years as we have developed a Web 2.0 approach to openEHR clinical knowledge collaboration.
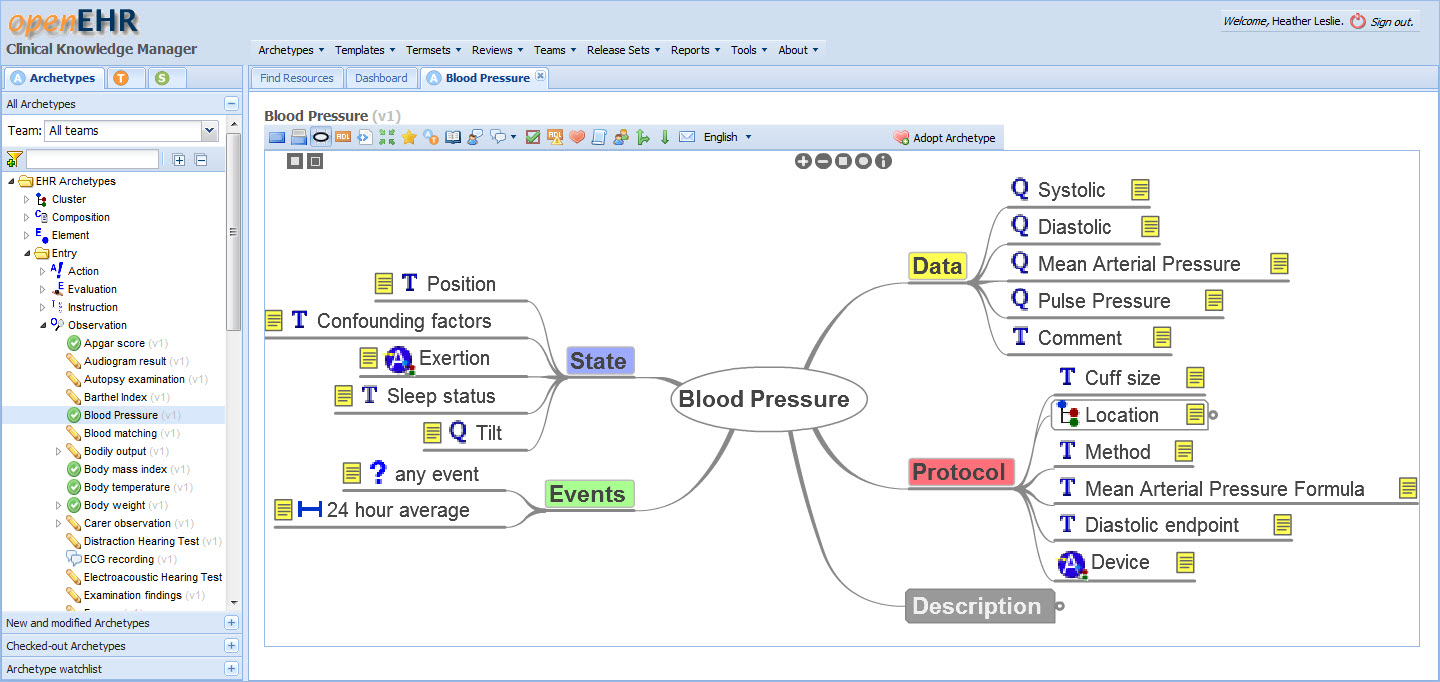
CKM is an international, online clinical knowledge repository providing digital asset management throughout the authoring, reviewing, publication and update lifecycle of these specifications. It has been designed to provide governance capabilities, and facilitates collaboration by registered participants. The full range of openEHR clinical knowledge resources - archetypes, templates and terminology subsets – are now managed in this environment.
...
Under the auspice of the openEHR Foundation, our goal is to offer a clinical knowledge management ecosystem in which: the knowledge artefacts are based on open specifications; the service and programming interfaces are openly specified; and the production data representations are also openly specified. Archetypes are freely available under a Creative Commons BY-SA license.
The focus of CKM to date has been to publish a coherent set of archetypes that can be use by national body or health application developers in projects that involve shared EHRs. These archetypes have developed in different projects, including work in partnership with the Nasjonal IKT (Norway), UK NHS, Australian and Swedish eHealth Programs and in collaboration with clinical application developers building working systems.
The intent for current CKM archetype design is to make it possible for them to be used across any and all clinical systems - 'global' archetypes. By design these archetypes:
...
The draft archetypes currently in CKM do not meet all these requirements but as they progress through the publication process are brought closer to this ideal. As requirements develop (and health care changes) the archetypes will be revised always seeking to maintain universal sharing of the very important health information held in a lifelong record.
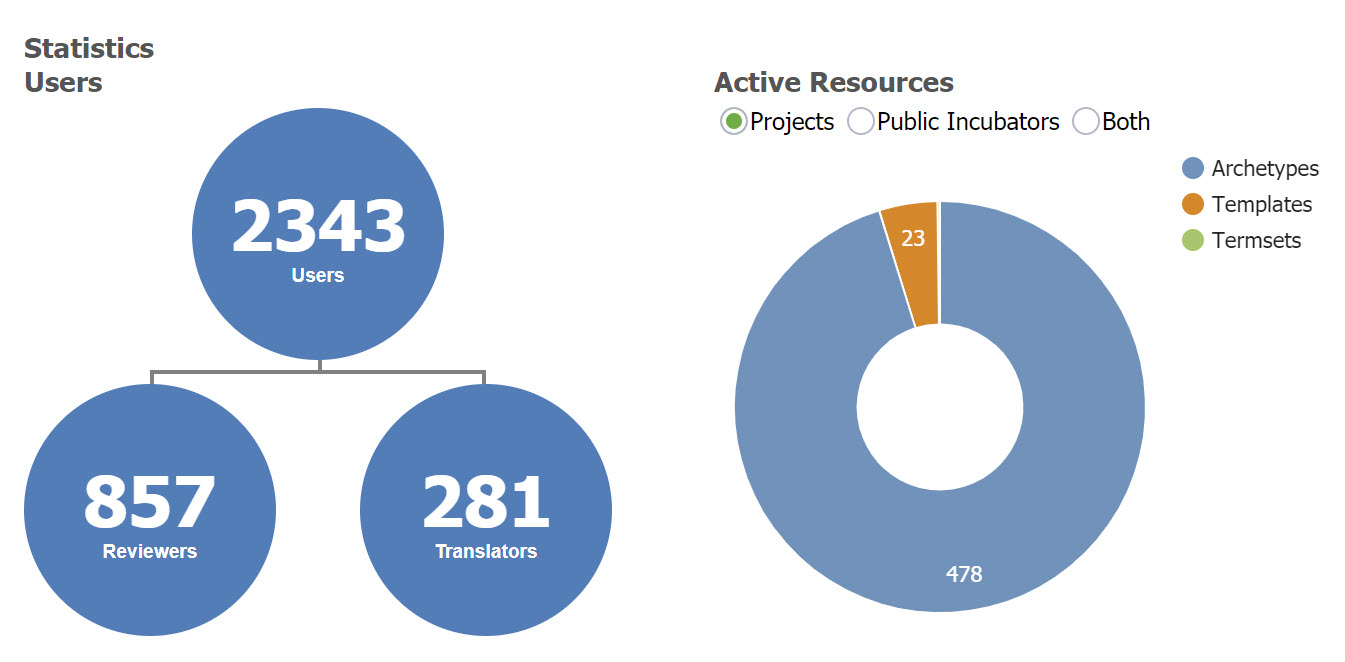
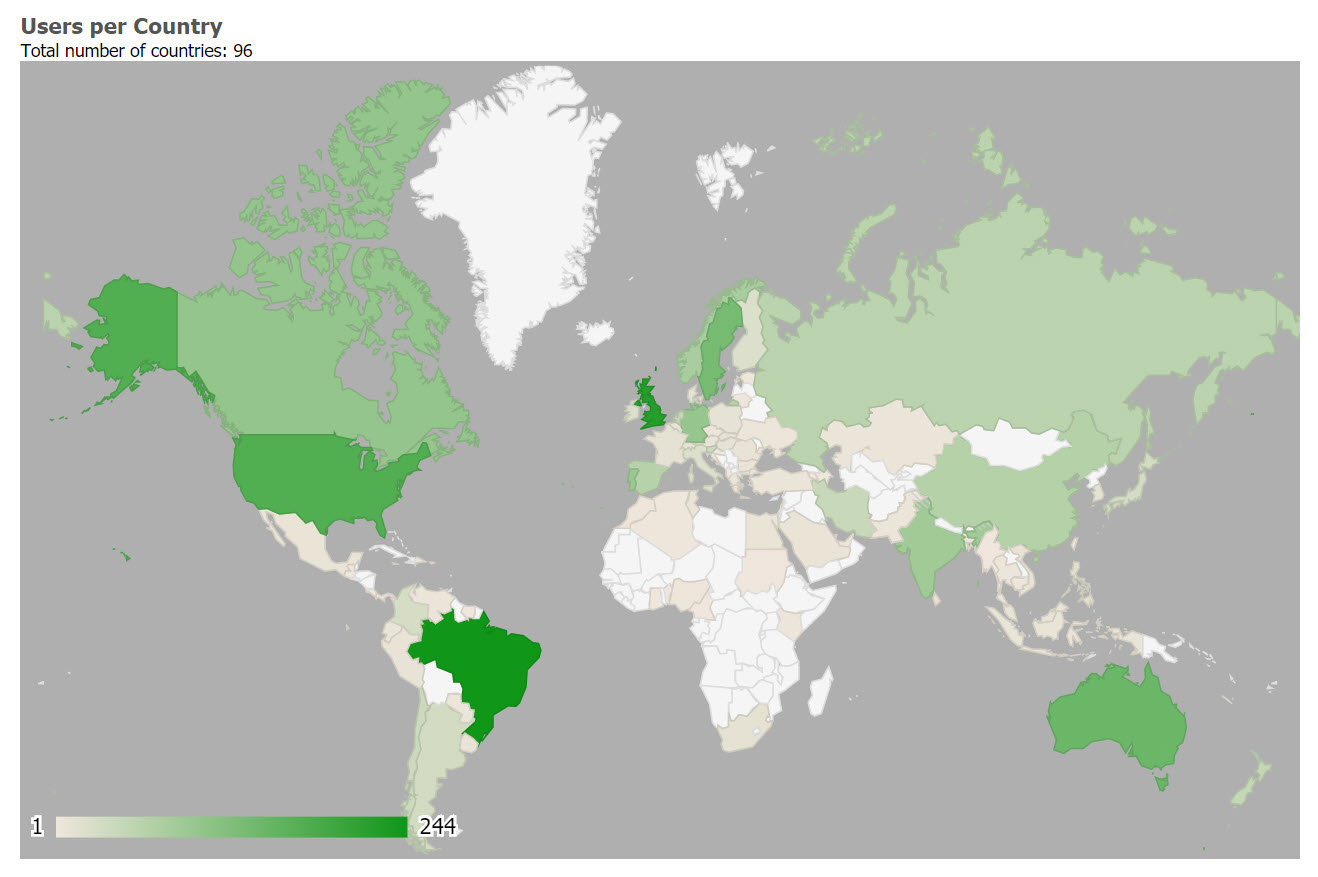
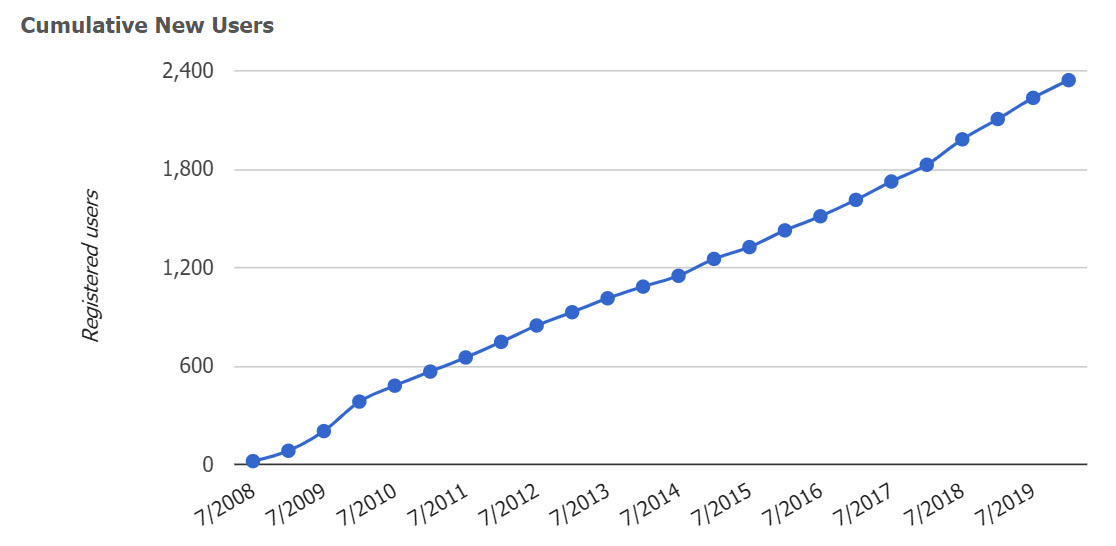
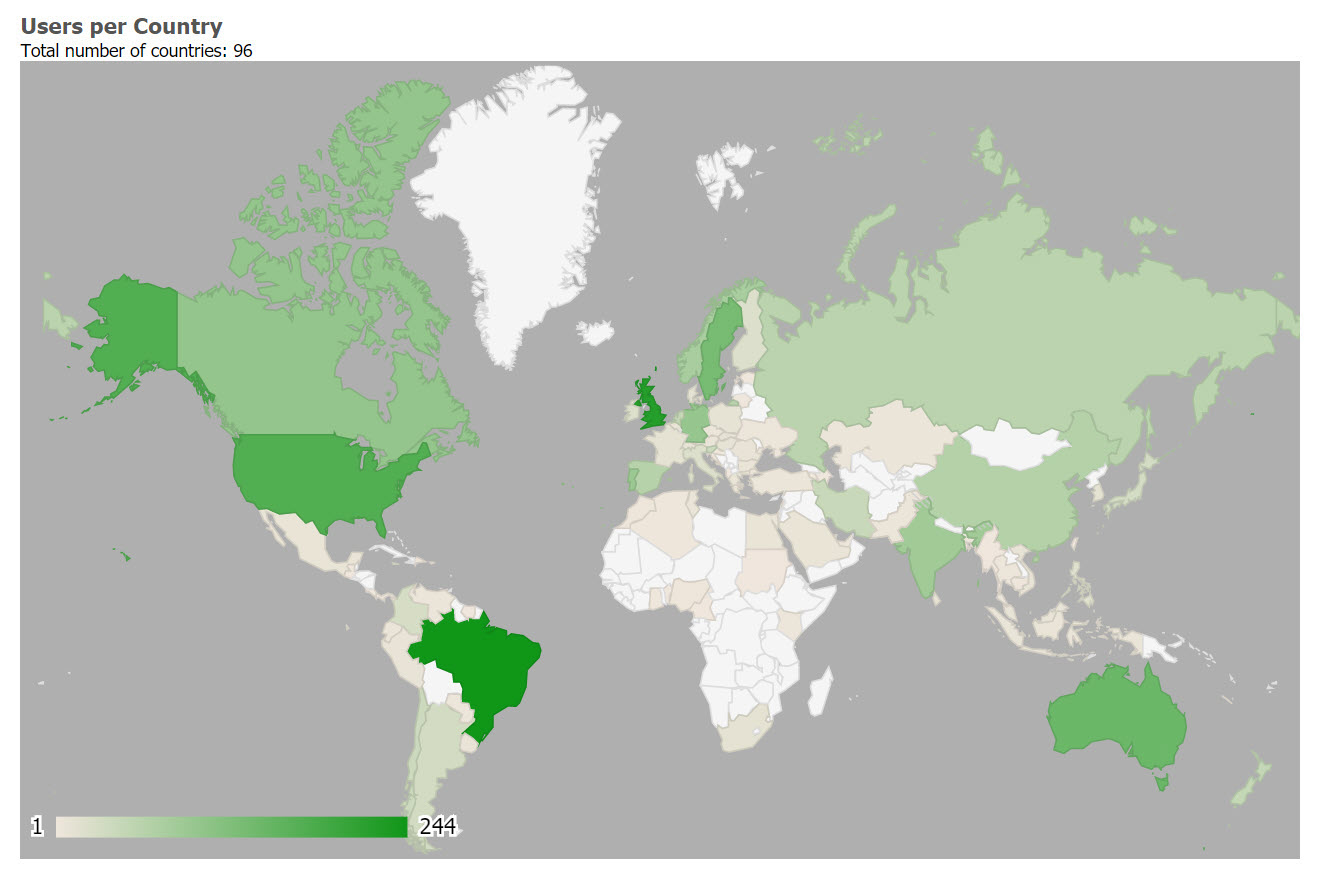
As of November, 2019 CKM has acquired, largely by word of mouth, 2343 registered users from 96 countries, including 857 people who have volunteered to review archetypes, and 281 who have volunteered to translate archetypes. The repository contains 478 archetypes, of which 92 are currently published (11%). 23 templates have been uploaded, mainly as examples of clinical data set content.
Current CKM functionality includes:
...
- Display of artefacts including structured views, technical representations and mind maps to make it easy for clinicians and others to review;
- Uploading of new knowledge artefacts – archetypes, templates and terminology subsets – for review and publication;
- Archetype metadata supporting classification, ontological relationships and repository-wide searches;
- Digital asset management including provenance and artefact audit trail;
- Integration with openEHR tools supporting quality assessment & technical validation checks;
- Review and publication process for clinical content – draft, team review, published and reassess states
- Terminology binding and terminology subset reviews;
- Online archetype translation with review;
- Community engagement via threaded discussions, repository downloads, attached resources, watch lists, email notifications, user dashboards and release sets;,
- Editorial support via do lists, user and team administration, review management, artefact modification, classification management, broadcast emails etc;
- Subscriber auto-notification including Twitter and email
- Reports – Archetypes, Templates and Registered users
Transparency is a key principle within CKM. Editors are accountable to the community at every step; all comments, review rounds, changes etc. within CKM can be seen by the users. This ensures that if a user flags an issue, it is managed publicly and the user community can comment on the resolution.
...
Perhaps most important is what has been learned about knowledge governance – a relatively new domain. We anticipated complexity and the more we advance the CKM tool, the more we discover! This is an exciting and challenging journey.
We are ready now to encourage and embrace greater participation - harnessing the collective intelligence of the CKM community - through development of an archetype 'pool' where users can share their work on archetypes, templates and terminology subsets - a stepping stone into the tightly governed 'global' archetype pool. Some of these community archetypes will be developed for other purposes than the 'maximal data set, universal use case' scenario and provide valuable intermediate steps to support existing protocols and work to be used in a shared health record. We want to enable these to be shared and reused while at the same time encouraging work towards more general and broadly shareable solutions – all will benefit if we can share and learn from each other.
...